|
Fitness Blog Covering Topics Of Interest Tuesday, December 31 2013
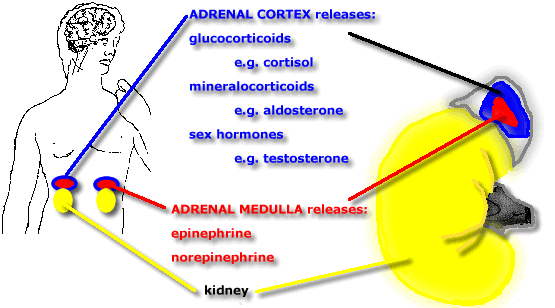
One night, you're in a bad neighborhood. A grungy thug comes out of nowhere and starts chasing you down the block. Suddenly, you are able to run faster and longer than you thought you ever could. And this is because your sympathetic nervous system has taken charge, which stimulates your adrenal glands to work harder. But say you have a work assignment that is due the next day, the baby is crying even though you need to get dinner ready for your guests, your other child is screaming at you, and the TV is on full blast in the other room. Your body still interprets this as being under severe stress. The sympathetic nervous system has a hard time shutting off, the adrenal glands are overworking, and problems occur. Unfortunately, modern life often has overstimulation and a lot of pressures and difficulties that keep the sympathetic nervous system in fight-or-flight mode continually. So where exactly are the adrenal glands? The kidneys are located in the lower back region, right around the second lumbar section of the spine just under your waistline, depending on the person. The adrenal glands are situated right above the kidneys. The body is a whole universe with an extensive communication network. The body's nervous system breaks down into two parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The autonomic nervous system is part of the peripheral nervous system. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for involuntary movements and actions. It controls heartbeats, breathing, digesting, sweating, crying, etc. It is divided into the sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system controls the fight-or-flight response. This means how your body responds to emergency and stressful situations. When the sympathetic nervous system is switched on your parasympathetic nervous system is switched off so that your body can cope with the emergencies more efficiently. When the sympathetic nervous system is on your heart rate increases, you sweat, your pupils dilate, and your body shuts down your digestion system so that it can focus on dealing with the emergency. The parasympathetic nervous system kicks in when the sympathetic nervous system switches off. Your heart rate returns to normal, your digestion system starts back up, and body functions return to normal. Although the nervous system's main communicators as neurons, the endocrine system's main communicators are chemical messengers known as hormones. Hormones are carried in the bloodstream to specific areas of the body, including organs and body tissues. Some of the most important endocrine glands include the pineal gland, the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, the thyroid, the ovaries, and the testes. When the sympathetic nervous system has been in flight-or-fight too long, it affects the hormones of the adrenal system. Too little or too much of the hormones can lead to adrenal fatigue and because of the way this fatigue impacts the body, it can lead to illness. This process of adrenal fatigue does not happen all at once. Instead, it is a gradual breakdown in the body. The Three Phases of Stress In 1956, endocrinologist Dr. Hans Selye developed a key concept in the study of stress and its effects on the body, which he termed, the general adaptation syndrome. In the general adaptation syndrome, the body passes through three phases in the way it copes with stress:
1. Alarm Phase This can cause those raised knotted shoulders, tight upper back and neck, chills along the spine, clammy hands, cold feet, increased heart rate, a tight locked pelvis, and tight leg muscles. A good example of this is in someone who has just had a car accident - a hugely stressful event. Just as their body responds to stress by causing the upper back and legs to tighten, the muscles are jerked quickly, causing injury that can take time to heal. On the other hand, the body does this to stay alive, so that the heart can keep pumping blood even under poor circumstances, and so the person won't feel pain as quickly - that's the beauty of the sympathetic nervous system's response. In the alarm phase, stress is relatively short lived and the return back to homeostasis is with ease. A list of what happens during a fight-or-flight response:
Symptoms: Shortness of breath, palpitations, emotional instability, headache, back pain, decrease in frequency and quantity of urination, insomnia, lack of appetite, dizziness, nausea, eye pain, cold hands and feet, tight neck and upper back muscles. Options on how to treat this stage:
2. Resistance Phase In the resistance phase, constantly reacting to stress leaves the body depleted, leading to a general decrease in overall resistance to illness, inflammation, and pain. Stress is wearing the body out even though the body is still resisting it. There is constant energy being sent by the adrenals and sympathetic nervous system to only the most important organs for a flight-or-fight circumstance. For example, since digestion is a parasympathetic function, undigested food begins to enter the colon, causing gas and bloating, and as the body can't pull the nutrients out of food as efficiently, there are less number of important nutrients to keep the body healthy and pain free. Secretion of the adrenal hormones is initially still high, but slows down as they begin to wear out. The sympathetic nervous system weakness leads to sympathetic deficiency. The parasympathetic nervous system begins to become more dominant as it attempts to compensate. The parasympathetic nervous system will switch on and take over, but not because the sympathetic nervous system has switched off, but because it's so exhausted that the parasympathetic nervous system has to pick up the slack so the body can function. What occurs is a constriction of blood vessels such as capillaries and arteries in the brain, excitement of the digestive system, and adrenal gland deficiency along with a whole host of problems listed below. What happens during the Resistance Phase? What kind of patient has moved from the Alarm Phase to the Resistance Phase?
Symptoms:
Options on how to treat this stage: All the recommendations from Stage 1 will help, but here are a few more for the more severe stage 2. All of these should be checked out with a doctor first as you may be having more severe symptoms stemming from stress (for example, high blood pressure):
Stage 3: Exhaustion Stage Possible Consequences of Exhaustion Phase:
Sources - Bodymind Energetics Towards a Dynamic Model of Health. By Mark Seem, Ph.D. Sunday, April 07 2013
Legumes play an important role in traditional diets in many parts of the world. They are low in fat, are good sources of protein and fiber, and contain a variety of micronutrients and phytoestrogens (plant estrogens). Phytoestrogens have received a lot of attention for their ability to fight not only cancer, but also heart disease and osteoporosis. They help balance hormones in the body and thus are thought to be particularly valuable for the hormone-dependent cancers: breast cancer and prostate cancer. It is well known that male hormones play a role in prostate cancer development. Despite their advantages, legumes play a minor role in most Western diets. The typical Western based diet (lower in vegetables and legumes and higher in animal-based foods) can cause an increase in both male and female hormones (androgens and estrogens), while a plant-based diet tends to lower these hormones. This is the basis for the role of diet in the development of hormone-dependent cancers. Soy foods, such as tofu, soy milk, soy beans, and vegetarian burgers, seem to be particularly rich in cancer-fighting properties. This is at least partially due to a form of phytoestrogen, called isoflavones, that is found primarily in soy. It appears to help prevent prostate cancer by binding to male hormone receptors in the prostate, thus reducing the stimulating effect of male hormones on prostate cell growth. Epidemiological studies have shown that high levels of isoflavones are often associated with low rates of breast, colon, and prostate cancer. This has been used to explain why countries such as Japan and China that typically consume large amounts of soy have lower risks of these diseases. The difficulty with consuming soy for reducing risk of prostate cancer is the lack of clinical trial evidence to support its use. As with any dietary component, it is difficult to isolate the effect of a particular food type to prove its effectiveness. One prospective study, including over 12,000 men, did evaluate consumption of soy milk. It found that those who drank soy milk regularly had a reduced risk of prostate cancer. The relationship held up after other factors were controlled for. Other studies need to be done to further establish the benefits of soy. In the meantime, getting more soy foods into your diet can be healthy for many reasons, and lowering your risk of prostate cancer may be one of these. Wednesday, March 13 2013
The prostate gland depends on testosterone for growth and development. Prostate cells, both noncancer and cancer, do too. This is why prostate cancer is sometimes referred to as a hormone-dependent cancer. Higher levels of circulating testosterone lead to higher concentrations in the prostate, and this appears to increase the risk of clinically significant prostate cancer. However, higher testosterone levels are not consistently found in prostate cancer patients, so there is more to the relationship. A possible protective role of exercise has been proposed based on its ability to lower testosterone levels and to boost the immune system. Exercise causes a temporary reduction in testosterone, so regular exercise can reduce long-term exposure to testosterone. And chronic exercise has been shown to increase the number and activity of natural killer cells, which are part of the immune system that attack cancer cells. Based on these effects, it seems that exercise should be beneficial, but the evidence concerning the impact of exercise on prostate cancer risk is inconclusive. In a review of 17 epidemiological studies of varying quality, 9 showed a beneficial effect, 5 no effect, and the other 3 actually showed an increased risk related to exercise or physical activity. None of the studies, however, provided conclusive proof, but taken together, they seem to support a weak beneficial effect of regular exercise on prostate cancer risk. The challenge is proving that men who exercise regularly develop less prostate cancer when all other factors are the same. This requires a prospective long-term randomized study, and this probably will never be done. The best long-term prospective studies that looked at habitual physical activity in adulthood are encouraging, however. A study of nearly 18,000 alumni of Harvard University showed that those who maintained a high level of physical activity were about half as likely to develop prostate cancer after the age of 70 as those who were least active. Another prospective study evaluated the level of physical fitness, as well as physical activity, on the risk of prostate cancer. Higher fitness levels were associated with lower risk in men under 60, but not in older men. And men who expended more than 1,000 kcal per week in exercise had lower risk than those who did not get this much exercise. The best long-term study of men's health is the Health Professionals Follow-up Study. It began in 1986 and has followed over 47,000 men in various health occupations since then. Data was collected in the beginning, and periodically through the study, on many factors including physical activity. The only positive result through 1994 was that at least 3 hours per week of vigorous physical activity was associated with a reduced risk of metastatic prostate cancer. But no relationship was observed between physical activity and the incidence of total or advanced prostate cancer. The same study, however, found an inverse relation between physical activity and BPH, more activity meant a lower likelihood of urinary symptoms or surgery for BPH. Walking 2–3 hours per week was enough to lower the risk of BPH. The bottom line is that questions remain about the relation between exercise and prostate cancer, but there is no question that regular exercise is good for general health. So, it is wise to get some moderate exercise on most days of the week, and you may be protecting yourself from prostate problems, too. |
 |