|
Fitness Blog Covering Topics Of Interest Thursday, July 16 2015
Mobility — the ability to move purposefully around your environment — is vitally important to health and well-being. Nearly one-third to one-half of adults ages 65 and older experience impaired mobility. At first, it may not seem like a big deal — many people with impaired mobility learn to just move a little more slowly and a little more deliberately. Some people work around the problem by relying on a cane or walker. That’s why it’s important to intervene to either prevent future mobility impairments or reduce existing ones.But taking impaired mobility “lying down” can cause your health to spiral downward. As you move less, pounds may start to creep on. You might withdraw from social relationships and activities that challenge you mentally. Exercise may become difficult, and lack of activity can worsen many health problems. This cycle of physical, emotional, and mental decline further restricts mobility. For most people, the ability to rely on their own bodies, skills, and mental agility is a crucial part of living a satisfying life. Having full mobility helps you fully engage with the world and fosters a sense of self-sufficiency that can help you live independently well into your later years. Thursday, March 06 2014
With so many types of hearing aids on the market, which one is right for you? The answer depends on many things. The main consideration is the nature of your hearing loss, its cause, and its severity. The results of your hearing tests will guide your audiologist or hearing aid specialist in making recommendations. Here are seven things you should know as you evaluate your options.
Thursday, January 23 2014
Even the healthiest people can find it hard to stick with an exercise regimen — and if you suffer from the joint pain of arthritis, moving your body may be the last thing you want to think about. But regular exercise not only helps maintain joint function, but also relieves stiffness and reduces pain and fatigue. If you have arthritis, you want to be sure your exercise routine has these goals in mind:
Arthritis doesn’t have to keep you from enjoying life. Monday, January 07 2013
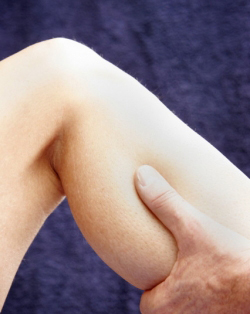 © Betty Shepherd
Sports massage is a form of massage therapy that is tailored to treat the needs of athletes. The use and application of specific techniques is the foundation of sports massage, yet what distinguishes it from other modalities is the intention behind the therapy. Many of us might think of massage as relaxing and holistic. Sports massage, in contrast, is designed to achieve specific goals, such as increasing performance or treating or preventing injury. The purpose of a sports massage session can vary, depending upon numerous factors that are unique to each athlete. For instance, sports massage can be used effectively to treat conditions such as tendonitis, strains, sprains, and adhesions. It can also be used in conjunction with training schedules and conditioning programs to enhance performance, aid in recovery and reduce the potential for injuries. The major applications of sports massage are recovery, remedial (to improve a debilitating condition), maintenance, and event (pre, inter, and post). An athlete can enhance his or her performance by knowing when to incorporate sports massage into a training routine. Healthy, injury-free muscles perform better, longer, and with less chance of injury. Sports massage can help to optimize the positive factors that affect performance, such as healthy muscle and connective tissues, normal range of motion, high energy and fluid and pain-free movement, as well as inducing mental calm and improving alertness, and concentration. It also can help minimize negative factors such as dysfunctional muscle and connective tissue, restricted range of motion, low energy, staleness, pain, and high anxiety(1a). Sports massage decreases injury potential by helping to prevent acute injuries (muscle tears) as well as chronic injuries stemming from wear and tear (tendonitis). Regular massage allows the muscles and soft tissue to stay supple and healthy, lengthened and flexible and free from adhesions, thereby reducing the potential for injury. By increasing circulation and assisting the body’s healing processes and breaking down scar tissue and adhesions, sports massage can help chronic injuries get better. Important Primary and Secondary Effects of Sports Massage(1b)Primary effects refer to the physiological and psychological condition of the athlete and include:
Secondary effects refer to performance-related outcomes and include:
If you decide that sports massage is the right treatment for you, it is important to find a well-trained therapist. Check out if a practitioner has had training in sports massage from an accredited school. Currently, there is no national credentialing that signifies a person who has passed a test demonstrating a solid understanding of the foundations and techniques of sports massage, so you will have to ask a few questions. How many hours of training (in general) did they have? Was their school accredited by the American Massage Therapy Association? How many hours of training in sports massage did they receive? What kind of athletes have they worked with? Were the athletes training or competing at the time? Is your therapist an athlete (on any level)? Many sports massage practitioners participate in races or competitive events, which increases their understanding not only of the uses and benefits of sports massage, but of other factors that go into being an athlete. For example, the length of time between the massage session and the athletic event directly relates to the depth of pressure a therapist should use. A knowledgeable therapist will know that a pre-event massage, which is meant to encourage general looseness, calls for less deep work than a regular “maintenance” massage. It is important that your therapist always errs on the side of caution when using deep pressure, and that they have an understanding of the psychology of an athlete and the physical demands of training. One of the benefits of working regularly with the same sports massage therapist is that he or she can learn to feel what is “normal” for your tissue and body type and can keep a watchful eye on any changes that may signal the need to head off potential trouble spots. If an injury does occur, the therapist can join the team of health care practitioners helping you to recover. Here, the focus is on healing the injury quickly and effectively, minimizing the side effects of the injury and decreasing the chance of re-occurrence. The use of sports massage in training routines varies depending on the athlete, the sport being trained for and the level of competition. It is important to mention that every athlete and every situation is going to be different, and that each person should research and find a plan that is most suitable for them. With that in mind, let’s take a look at how two different athletes used sports massage in conjunction with their training. When Uta was competing in 5K to 10K races, or preparing for a marathon, she received sports massage twice a week. Usually, she scheduled her massages the day after one of her harder training sessions for the week. If that wasn’t possible, she would allow herself a treatment session on the same day as her hard workout, but she would wait at least 3 to 4 hours to let her body recover some from the training before addressing soft tissue needs. Getting regular massage during her intense training periods also helped Uta psychologically, by allowing her to give back to her body and take some time for herself. Training for my first triathlon, I used sports massage regularly. I noticed that I could identify potential problems and head them off before they became an impediment in my training. I also felt, during the most intense training periods, that taking the time to give back to my body really helped me to feel like I was rounding out my training program. Having time to recover, making the effort to work my muscles and being in tune with my body, all played integral roles in my ability to train as hard as I did, without hurting myself. Getting regular massages during training is a great way to generate feedback for yourself about how you are doing. The more feedback you can gather about performance and training, and how your body is responding to it all, the better informed you will be about how you can compete and recover from competition. Sports massage, therefore, can be a great tool for athletes in their training. It provides myriad benefits, including increasing performance potential, speeding recovery time, and reducing the prevalence of injuries. And let’s not forget the wonderful relaxation, stress relief, and whole body integration that everyone—not just the athlete—can obtain from massage! |
 |