|
Fitness Blog Covering Topics Of Interest Thursday, November 26 2015
In his Autumn 2015 statement, the Chancellor pledges to spend £600m on mental health. Out comes the fan fare and heaps and loads of praise for him and his party on tackling the current unacceptable under funded mental health situation in England. Let us, for a moment, step back and open the history books and look at mental health funding in England since 2010; the time when George Osborne, our Chancellor took office. Funding for NHS trusts to provide mental health services has fallen by more than 8% in real terms since 2010, according to research by Community Care and BBC News. Figures obtained under the Freedom of Information Act from 43 mental health trusts in England show that total funding for the trusts’ mental health services dropped in real terms by 8.25 per cent, or almost £600m (once inflation has been accounted for). Now, after a reality check has been taken of the situation should we still be showering the Chancellor with praise for his generosity?. In real terms, the Chancellor has been cutting funding to the most vulnerable persons in society, the mentally ill by £600m over the last 5 years and now we expect them to be thankful that he's giving it back. What sort of society do we live in where we make the most vulnerable suffer by not providing adequate services for them?. All that the Chancellor has done is to put mental health in England back to where it was in 2010 when he became chancellor and society should be grateful for this?. Gym In Motion provides fitness programs to persons struggling with mental health illness. What we've seen over the past 5 years is the impact that the taking of £600m in cuts from the mental health services has had on the most vulnerable in society. Front line services being strained to their maximum, long waiting lines to access therapy while the majority of people with mental health issues just don't get any help at all. Society is denying these vulnerable people assistance in the name of saving money. Not only have I experienced this from a supplier's point of view, but from first hand experience as I have a number family members who suffer or have suffered with mental health illness over the years. No where, has any government minister, employee or consultant, looked behind the scenes and seen that by denying services to a person with a mental health illness, in most cases causes their mental state of mind to worsen and so they spiral into deteriation. These are the consequences that are just brushed under the carpet, the consequences that aren't mentioned at dinner parties for they force society to take note of their actions which is not a pretty sight. Somehow, I don't think that those with a mental health illness will be heralding our Chancellor for giving back to the mental health services, what was rightly there's in the first place. If I'm a cynical person, I'd say that this whole announcement was just for our Chancellor and government of the day to get brownie points and be seen to do something about a dire situation which they created in the first place. The uninformed will be thankful, the informed will not be amused. References: Friday, November 06 2015
You might be eager to leap into your exercise routine and get on with the day — but don’t just dive in. Starting a workout with “cold” muscles can lead to injury. It’s important to start each workout with a warm-up and end with a cool-down — and that goes for true beginners, seasoned pros, and everyone in between. Warm-upWarming up pumps nutrient-rich, oxygenated blood to your muscles as it speeds up your heart rate and breathing. A good warm-up should last five to 10 minutes and work all major muscle groups. For best results, start slowly, then pick up the pace. Many warm-up routines focus on cardio and range-of-motion exercises, such as jumping jacks and lunges. If you prefer, you can do a simpler warm-up by walking in place while gently swinging your arms, or even dancing to a few songs. Cool-downAfter your workout, it’s best to spend five to 10 minutes cooling down through a sequence of slow movements. This helps prevent muscle cramps and dizziness while gradually slowing your breathing and heart rate. An effective cool-down also incorporates stretching exercises to relax and lengthen muscles throughout your body and improve your range of motion. To get the most out of these exercises, hold each stretch for 10 to 30 seconds. The longer you can hold a stretch, the better for improving your flexibility. As with the warm-up, it’s best to flow from one stretch to the next without rests in between. Wednesday, October 28 2015
Your bone strength and size peaks by age 30. After that, bones tend to become less dense, making them more fragile and subject to Even if you’re older, exercise is still a great way to protect your bones. The physical stress placed on bones during exercise stimulates the growth of new bone tissue. The type of exercise you do matters. To bolster your bones, you need to get regular weight-bearing exercise. This includes weight lifting and resistance training, as well as any type of activity that forces you to work against gravity by standing or carrying your body’s weight, including running, walking, dancing, and stair climbing. Activities such as swimming or biking aren’t weight-bearing and thus don’t build bone. Generally, higher-impact activities (such as running) or resistance exercises (such as strength training) have a more pronounced effect on bone than lower-impact exercises, such as walking. Only the bones that bear the load of the exercise will benefit. For example, running protects bones in the hips and legs, but not the arms. A well-rounded strength training plan can benefit practically all of your bones. Because exercise improves your overall strength, coordination, and balance, it also makes you less likely to fall, which means less opportunity to break a bone. To read more about the many benefits of exercise and learn how to start an exercise program that works for you, contact Ronald on 07929 256856. Monday, October 05 2015
The next time you have a check-up, don’t be surprised if your doctor hands you a prescription to walk. Yes, this simple activity that you’ve been doing since you were about a year old is now being touted as “the closest thing we have to a wonder drug,” in the words of Dr. Thomas Frieden, director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Of course, you probably know that any physical activity, including walking, is a boon to your overall health. But walking in particular comes with a host of benefits. Here’s a list of five that may surprise you. 1. It counteracts the effects of weight-promoting genes. Harvard researchers looked at 32 obesity-promoting genes in over 12,000 people to determine how much these genes actually contribute to body weight. They then discovered that, among the study participants who walked briskly for about an hour a day, the effects of those genes were cut in half. 2. It helps tame a sweet tooth. A pair of studies from the University of Exeter found that a 15-minute walk can curb cravings for chocolate and even reduce the amount of chocolate you eat in stressful situations. And the latest research confirms that walking can reduce cravings and intake of a variety of sugary snacks. 3. It reduces the risk of developing breast cancer. Researchers already know that any kind of physical activity blunts the risk of breast cancer. But an American Cancer Society study that zeroed in on walking found that women who walked seven or more hours a week had a 14% lower risk of breast cancer than those who walked three hours or fewer per week. And walking provided this protection even for the women with breast cancer risk factors, such as being overweight or using supplemental hormones. 4. It eases joint pain. Several studies have found that walking reduces arthritis-related pain, and that walking five to six miles a week can even prevent arthritis from forming in the first place. Walking protects the joints — especially the knees and hips, which are most susceptible to osteoarthritis — by lubricating them and strengthening the muscles that support them. 5. It boosts immune function. Walking can help protect you during cold and flu season. A study of over 1,000 men and women found that those who walked at least 20 minutes a day, at least 5 days a week, had 43% fewer sick days than those who exercised once a week or less. And if they did get sick, it was for a shorter duration, and their symptoms were milder. Thursday, July 16 2015
Mobility — the ability to move purposefully around your environment — is vitally important to health and well-being. Nearly one-third to one-half of adults ages 65 and older experience impaired mobility. At first, it may not seem like a big deal — many people with impaired mobility learn to just move a little more slowly and a little more deliberately. Some people work around the problem by relying on a cane or walker. That’s why it’s important to intervene to either prevent future mobility impairments or reduce existing ones.But taking impaired mobility “lying down” can cause your health to spiral downward. As you move less, pounds may start to creep on. You might withdraw from social relationships and activities that challenge you mentally. Exercise may become difficult, and lack of activity can worsen many health problems. This cycle of physical, emotional, and mental decline further restricts mobility. For most people, the ability to rely on their own bodies, skills, and mental agility is a crucial part of living a satisfying life. Having full mobility helps you fully engage with the world and fosters a sense of self-sufficiency that can help you live independently well into your later years. Friday, September 05 2014
Fruits and vegetables contain vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients that are essential for good health. That’s one reason why a plant-based diet that includes lots of fruits and vegetables can lower your risk of developing life-threatening diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and some cancers. And when you pile on the produce, there’s less room for the unhealthy foods. Dinner is typically the largest (and latest) meal of the day, and it’s a good opportunity to make sure that you meet your daily quota for fruits and vegetables. Here are five easy ways to work more produce into dinner.
Thursday, August 21 2014
If opening jars becomes more difficult because of painful hands, or if climbing stairs produces pain in your knees, “arthritis” is often the first thing that comes to mind. The two most common forms of arthritis—osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis—can cause similar aches and pains, but there are a few key differences between them. For example: Onset. Osteoarthritis occurs when cartilage (tissue in your joints that cushions your bones) wears away. Pain occurs when bone rubs against bone. This type of arthritis pain tends to develop gradually and intermittently over several months or years. Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis affecting 27 million Americans. Many people believe it’s a crippling and inevitable part of growing old. But things are changing. Treatments are better, and plenty of people age well without much arthritis. If you have osteoarthritis, you can take steps to protect your joints, reduce discomfort, and improve mobility — all of which are detailed in this report. If you don’t have osteoarthritis, the report offers strategies for preventing it. Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is an inflammatory condition in which your immune system attacks the tissues in your joints. It causes pain and stiffness that worsen over several weeks or a few months. And joint pain isn’t always the first sign of rheumatoid arthritis—sometimes it begins with “flu-like” symptoms of fatigue, fever, weakness, and minor joint aches. Location. Both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can affect the hands. However, osteoarthritis often affects the joint closest to the tip of the finger, whereas rheumatoid arthritis usually spares this joint. And while rheumatoid arthritis can appear in any joint, its most common targets are the hands, wrists, and feet. Type of stiffness. People often describe vague muscle aches as “stiffness,” but when doctors talk about “stiffness,” they mean that a joint doesn’t move as easily as it should. Stiffness may be prominent even when joint pain is not. Mild morning stiffness is common in osteoarthritis and often goes away after just a few minutes of activity. Sometimes people with osteoarthritis also notice the same type of stiffness during the day after resting the joint for an hour or so. In rheumatoid arthritis, however, morning stiffness doesn’t begin to improve for an hour or longer. Occasionally, prolonged joint stiffness in the morning is the first symptom of rheumatoid arthritis. Thursday, July 24 2014
Medications make a difference — generally a positive one — in the lives of many people. Insulin keeps blood sugar under control, cholesterol-lowering drugs can reduce the chances of having a heart attack, and thyroid medication can restore a normal hormone level. These are but a few examples. At the same time, all drugs carry side effects, and can interact with other medications. For many medications, one or more side effects affect balance. And that can increase your chances of taking a fall. How? According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, common problems include vision changes, dizziness or lightheadedness, drowsiness, and impaired alertness or judgment. Some medications may damage the inner ear, spurring temporary or permanent balance disorders. How do I know if this is a problem for me?Some of the commonly prescribed medications that can affect balance include:
Sometimes the problem isn’t a single drug but the combination of medications being taken together. Older adults are especially vulnerable, because drugs are absorbed and broken down differently as people age. If you are concerned about how your medications may be affecting your balance, call you doctor and ask to review the drugs you’re taking, the dose, and when you take them. It is never a good idea to just stop taking a medication without consulting your health care provider first. Doing so can create even more health risks. Thursday, May 15 2014
The prostate is can be a troublesome little gland. It is prone to painful infections and inflammation (prostatitis), enlargement that interferes with urination (benign prostatic hyperplasia, or BPH), and cancer. Prevention is the best medicine, something exercise can help with. Exercise has also been shown to help treat various prostate-related conditions. Although relatively few studies have looked at the impact of exercise specifically on prostate health, the ones that have suggest that regular physical activity can be good for this walnut-sized gland. BPH prevention. In the ongoing Harvard-based Health Professionals Follow-up Study, men who were more physically active were less likely to suffer from BPH. Even low- to moderate-intensity physical activity, such as walking regularly at a moderate pace, yielded benefits. Prostatitis treatment. Italian researchers conducted a randomized controlled trial (considered the gold standard of medical research) in men with chronic prostatitis. Those in the aerobic exercise group walked briskly three times a week. A comparison group did non-aerobic exercise (leg lifts, sit ups, and stretching) three times a week. At the end of 18 weeks, men in both groups felt better, but those doing aerobic exercises reported less prostatitis pain, less anxiety and depression, and better quality of life. Prostate cancer progression. In a study of more than 1,400 men diagnosed with early-stage prostate cancer, men who walked briskly (not leisurely) for at least three hours a week were 57% less likely to have their cancer progress than those who walked less often and less vigorously. In an analysis from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study, men diagnosed with localized prostate cancer who engaged in vigorous activity at least three hours each week had a 61% lower chance of dying from the illness, compared to men who engaged in vigorous activity less than one hour a week. How to get started A well-rounded exercise program that includes a half-hour of physical activity on all or most days of the week delivers solid health benefits. And you needn’t perform this activity all at once; you can break it up into three 10-minute segments. As always, talk to your doctor before beginning an exercise program. He or she can help you develop a routine based on your health and fitness level. Thursday, January 23 2014
Even the healthiest people can find it hard to stick with an exercise regimen — and if you suffer from the joint pain of arthritis, moving your body may be the last thing you want to think about. But regular exercise not only helps maintain joint function, but also relieves stiffness and reduces pain and fatigue. If you have arthritis, you want to be sure your exercise routine has these goals in mind:
Arthritis doesn’t have to keep you from enjoying life. Tuesday, December 31 2013
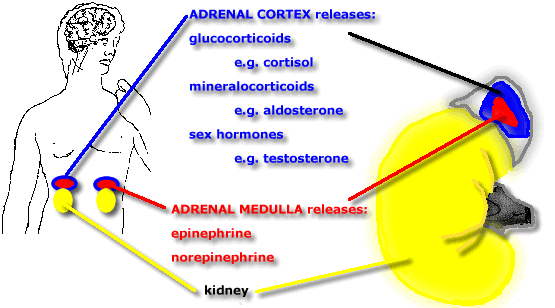
One night, you're in a bad neighborhood. A grungy thug comes out of nowhere and starts chasing you down the block. Suddenly, you are able to run faster and longer than you thought you ever could. And this is because your sympathetic nervous system has taken charge, which stimulates your adrenal glands to work harder. But say you have a work assignment that is due the next day, the baby is crying even though you need to get dinner ready for your guests, your other child is screaming at you, and the TV is on full blast in the other room. Your body still interprets this as being under severe stress. The sympathetic nervous system has a hard time shutting off, the adrenal glands are overworking, and problems occur. Unfortunately, modern life often has overstimulation and a lot of pressures and difficulties that keep the sympathetic nervous system in fight-or-flight mode continually. So where exactly are the adrenal glands? The kidneys are located in the lower back region, right around the second lumbar section of the spine just under your waistline, depending on the person. The adrenal glands are situated right above the kidneys. The body is a whole universe with an extensive communication network. The body's nervous system breaks down into two parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The autonomic nervous system is part of the peripheral nervous system. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for involuntary movements and actions. It controls heartbeats, breathing, digesting, sweating, crying, etc. It is divided into the sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system controls the fight-or-flight response. This means how your body responds to emergency and stressful situations. When the sympathetic nervous system is switched on your parasympathetic nervous system is switched off so that your body can cope with the emergencies more efficiently. When the sympathetic nervous system is on your heart rate increases, you sweat, your pupils dilate, and your body shuts down your digestion system so that it can focus on dealing with the emergency. The parasympathetic nervous system kicks in when the sympathetic nervous system switches off. Your heart rate returns to normal, your digestion system starts back up, and body functions return to normal. Although the nervous system's main communicators as neurons, the endocrine system's main communicators are chemical messengers known as hormones. Hormones are carried in the bloodstream to specific areas of the body, including organs and body tissues. Some of the most important endocrine glands include the pineal gland, the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, the thyroid, the ovaries, and the testes. When the sympathetic nervous system has been in flight-or-fight too long, it affects the hormones of the adrenal system. Too little or too much of the hormones can lead to adrenal fatigue and because of the way this fatigue impacts the body, it can lead to illness. This process of adrenal fatigue does not happen all at once. Instead, it is a gradual breakdown in the body. The Three Phases of Stress In 1956, endocrinologist Dr. Hans Selye developed a key concept in the study of stress and its effects on the body, which he termed, the general adaptation syndrome. In the general adaptation syndrome, the body passes through three phases in the way it copes with stress:
1. Alarm Phase This can cause those raised knotted shoulders, tight upper back and neck, chills along the spine, clammy hands, cold feet, increased heart rate, a tight locked pelvis, and tight leg muscles. A good example of this is in someone who has just had a car accident - a hugely stressful event. Just as their body responds to stress by causing the upper back and legs to tighten, the muscles are jerked quickly, causing injury that can take time to heal. On the other hand, the body does this to stay alive, so that the heart can keep pumping blood even under poor circumstances, and so the person won't feel pain as quickly - that's the beauty of the sympathetic nervous system's response. In the alarm phase, stress is relatively short lived and the return back to homeostasis is with ease. A list of what happens during a fight-or-flight response:
Symptoms: Shortness of breath, palpitations, emotional instability, headache, back pain, decrease in frequency and quantity of urination, insomnia, lack of appetite, dizziness, nausea, eye pain, cold hands and feet, tight neck and upper back muscles. Options on how to treat this stage:
2. Resistance Phase In the resistance phase, constantly reacting to stress leaves the body depleted, leading to a general decrease in overall resistance to illness, inflammation, and pain. Stress is wearing the body out even though the body is still resisting it. There is constant energy being sent by the adrenals and sympathetic nervous system to only the most important organs for a flight-or-fight circumstance. For example, since digestion is a parasympathetic function, undigested food begins to enter the colon, causing gas and bloating, and as the body can't pull the nutrients out of food as efficiently, there are less number of important nutrients to keep the body healthy and pain free. Secretion of the adrenal hormones is initially still high, but slows down as they begin to wear out. The sympathetic nervous system weakness leads to sympathetic deficiency. The parasympathetic nervous system begins to become more dominant as it attempts to compensate. The parasympathetic nervous system will switch on and take over, but not because the sympathetic nervous system has switched off, but because it's so exhausted that the parasympathetic nervous system has to pick up the slack so the body can function. What occurs is a constriction of blood vessels such as capillaries and arteries in the brain, excitement of the digestive system, and adrenal gland deficiency along with a whole host of problems listed below. What happens during the Resistance Phase? What kind of patient has moved from the Alarm Phase to the Resistance Phase?
Symptoms:
Options on how to treat this stage: All the recommendations from Stage 1 will help, but here are a few more for the more severe stage 2. All of these should be checked out with a doctor first as you may be having more severe symptoms stemming from stress (for example, high blood pressure):
Stage 3: Exhaustion Stage Possible Consequences of Exhaustion Phase:
Sources - Bodymind Energetics Towards a Dynamic Model of Health. By Mark Seem, Ph.D. Saturday, October 05 2013
This quick and simple salad is a delicious solution to the age-old question, “What’s for dinner?” It’s filled with wholesome ingredients, protein and fiber to enhance your hard earned fitness results. Servings: 6 For the Salad
For the Dressing
Instructions
Nutritional Analysis: One serving equals: 218 calories, 12g fat, 189mg sodium, 5g carbohydrate, 4g fiber, and 22g protein Monday, April 22 2013
Our bodies can obtain vitamin D from diet and make it from sun exposure. Even with these two routes for obtaining vitamin D, however, inadequate vitamin D is common, and deficiencies can be found on all continents, in all ethnic groups, and across all ages—a major concern, given the many ways that vitamin D helps protect our health. () There are a number of factors that increase the risk of having inadequate vitamin D, among them, lifestyle, sunscreen use, geographic location, skin tone, age, and body weight.
The bottom line: Low vitamin D can be found in all ethnic and age groups, around the world, for a host of reasons. Even if you are taking a standard multiple vitamin, the amount of vitamin D in most vitamins (400 IU) is not enough to prevent low blood levels. If you suspect that you are at risk of vitamin D deficiency, you can ask your physician to order a blood test for vitamin D. Thursday, April 18 2013
Seasickness caused by boat motion can be a serious problem for sailors. Not only does the sick person feel terrible and become incapacitated, and therefore a problem too for others on a shorthanded boat, but the dehydration that may result from repeated vomiting can become a medical issue. Therefore it's important to know how to prevent seasickness. About 90% of people will experience seasickness or motion sickness at some point in their lives. If you're new to sailing, or have ever experienced nausea or dizziness on a boat, it's worthwhile to take steps early to prevent seasickness. Once seasickness occurs, it's too late to do much more than cope with it as best you can. Even with many medical studies and hundreds of years of experimenting with how to prevent seasickness, no one method or medication has been developed that works for everyone. But various methods do work for different people, so it's mostly an issue of taking the problem seriously and trying to determine what will work best for you. Prevention, Not CureSeasickness prevention remedies fall into four general categories: medications, food and drink prescriptions, wrist bands, and behavior tips: Medications
Note: if you have a health condition or are taking other medications, talk to your doctor before starting any new medication, to ensure the drugs do not produce a negative interaction. Food and Drink
Wrist Bands
Behavior Tips
Remember to Start Early!In most cases you should begin the remedy well before beginning to experience any signs or symptoms of seasickness. Usually that means before getting on the boat. But if you start out on a calm day and boat motion later starts to pick up, it's better late than never. Seasickness often begins with general feelings of drowsiness-the first sign may be yawning. Don't wait! Sunday, April 07 2013
Legumes play an important role in traditional diets in many parts of the world. They are low in fat, are good sources of protein and fiber, and contain a variety of micronutrients and phytoestrogens (plant estrogens). Phytoestrogens have received a lot of attention for their ability to fight not only cancer, but also heart disease and osteoporosis. They help balance hormones in the body and thus are thought to be particularly valuable for the hormone-dependent cancers: breast cancer and prostate cancer. It is well known that male hormones play a role in prostate cancer development. Despite their advantages, legumes play a minor role in most Western diets. The typical Western based diet (lower in vegetables and legumes and higher in animal-based foods) can cause an increase in both male and female hormones (androgens and estrogens), while a plant-based diet tends to lower these hormones. This is the basis for the role of diet in the development of hormone-dependent cancers. Soy foods, such as tofu, soy milk, soy beans, and vegetarian burgers, seem to be particularly rich in cancer-fighting properties. This is at least partially due to a form of phytoestrogen, called isoflavones, that is found primarily in soy. It appears to help prevent prostate cancer by binding to male hormone receptors in the prostate, thus reducing the stimulating effect of male hormones on prostate cell growth. Epidemiological studies have shown that high levels of isoflavones are often associated with low rates of breast, colon, and prostate cancer. This has been used to explain why countries such as Japan and China that typically consume large amounts of soy have lower risks of these diseases. The difficulty with consuming soy for reducing risk of prostate cancer is the lack of clinical trial evidence to support its use. As with any dietary component, it is difficult to isolate the effect of a particular food type to prove its effectiveness. One prospective study, including over 12,000 men, did evaluate consumption of soy milk. It found that those who drank soy milk regularly had a reduced risk of prostate cancer. The relationship held up after other factors were controlled for. Other studies need to be done to further establish the benefits of soy. In the meantime, getting more soy foods into your diet can be healthy for many reasons, and lowering your risk of prostate cancer may be one of these. Wednesday, March 13 2013
The prostate gland depends on testosterone for growth and development. Prostate cells, both noncancer and cancer, do too. This is why prostate cancer is sometimes referred to as a hormone-dependent cancer. Higher levels of circulating testosterone lead to higher concentrations in the prostate, and this appears to increase the risk of clinically significant prostate cancer. However, higher testosterone levels are not consistently found in prostate cancer patients, so there is more to the relationship. A possible protective role of exercise has been proposed based on its ability to lower testosterone levels and to boost the immune system. Exercise causes a temporary reduction in testosterone, so regular exercise can reduce long-term exposure to testosterone. And chronic exercise has been shown to increase the number and activity of natural killer cells, which are part of the immune system that attack cancer cells. Based on these effects, it seems that exercise should be beneficial, but the evidence concerning the impact of exercise on prostate cancer risk is inconclusive. In a review of 17 epidemiological studies of varying quality, 9 showed a beneficial effect, 5 no effect, and the other 3 actually showed an increased risk related to exercise or physical activity. None of the studies, however, provided conclusive proof, but taken together, they seem to support a weak beneficial effect of regular exercise on prostate cancer risk. The challenge is proving that men who exercise regularly develop less prostate cancer when all other factors are the same. This requires a prospective long-term randomized study, and this probably will never be done. The best long-term prospective studies that looked at habitual physical activity in adulthood are encouraging, however. A study of nearly 18,000 alumni of Harvard University showed that those who maintained a high level of physical activity were about half as likely to develop prostate cancer after the age of 70 as those who were least active. Another prospective study evaluated the level of physical fitness, as well as physical activity, on the risk of prostate cancer. Higher fitness levels were associated with lower risk in men under 60, but not in older men. And men who expended more than 1,000 kcal per week in exercise had lower risk than those who did not get this much exercise. The best long-term study of men's health is the Health Professionals Follow-up Study. It began in 1986 and has followed over 47,000 men in various health occupations since then. Data was collected in the beginning, and periodically through the study, on many factors including physical activity. The only positive result through 1994 was that at least 3 hours per week of vigorous physical activity was associated with a reduced risk of metastatic prostate cancer. But no relationship was observed between physical activity and the incidence of total or advanced prostate cancer. The same study, however, found an inverse relation between physical activity and BPH, more activity meant a lower likelihood of urinary symptoms or surgery for BPH. Walking 2–3 hours per week was enough to lower the risk of BPH. The bottom line is that questions remain about the relation between exercise and prostate cancer, but there is no question that regular exercise is good for general health. So, it is wise to get some moderate exercise on most days of the week, and you may be protecting yourself from prostate problems, too. Tuesday, March 05 2013
Vitamin D Deficiency: A Global ConcernIf you live north of the line connecting San Francisco to Philadelphia and Athens to Beijing, odds are that you don’t get enough vitamin D. The same holds true if you don’t get outside for at least a 15-minute daily walk in the sun. African-Americans and others with dark skin, as well as older individuals, tend to have much lower levels of vitamin D, as do people who are overweight or obese. Worldwide, an estimated 1 billion people have inadequate levels of vitamin D in their blood, and deficiencies can be found in all ethnicities and age groups. (-) Indeed, in industrialized countries, doctors are even seeing the resurgence of rickets, the bone-weakening disease that had been largely eradicated through vitamin D fortification. (-) Why are these widespread vitamin D deficiencies of such great concern? Because research conducted over the past decade suggests that vitamin D plays a much broader disease-fighting role than once thought. Being “D-ficient” may increase the risk of a host of chronic diseases, such as , , , and multiple sclerosis, as well as , such as and even the . Currently, there’s scientific debate about how much vitamin D people need each day. The Institute of Medicine, in a long-awaited report released on November 30, 2010 recommends tripling the daily vitamin D intake for children and adults in the U.S. and Canada, to 600 IU per day. () The report also recognized the safety of vitamin D by increasing the upper limit from 2,000 to 4,000 IU per day, and acknowledged that even at 4,000 IU per day, there was no good evidence of harm. The new guidelines, however, are overly conservative about the recommended intake, and they do not give enough weight to some of the latest science on vitamin D and health. For bone health and chronic disease prevention, many people are likely to need more vitamin D than even these new government guidelines recommend. Vitamin D Sources and FunctionVitamin D is both a nutrient we eat and a hormone our bodies make. Few , so the biggest dietary sources of vitamin D are fortified foods and . Good sources include dairy products and breakfast cereals (both of which are fortified with vitamin D), and fatty fish such as salmon and tuna. For most people, the best way to get enough vitamin D is taking a supplement, but the level in most multivitamins (400 IU) is too low. Encouragingly, some manufacturers have begun adding 800 or 1,000 IU of vitamin D to their standard multivitamin preparations. If the multivitamin you take does not have 1,000 IU of vitamin D, you may want to consider adding a separate vitamin D supplement, especially if you don’t spend much time in the sun. Talk to your healthcare provider. Two forms of vitamin D are used in supplements: vitamin D2 (“ergocalciferol,” or pre-vitamin D) and vitamin D3 (“cholecalciferol”). Vitamin D3 is chemically indistinguishable from the form of vitamin D produced in the body. The body also manufactures vitamin D from cholesterol, through a process triggered by the action of sunlight on skin, hence its nickname, “the sunshine vitamin.” Yet some people do not make enough , among them, people who have a darker skin tone, who are overweight, who are older, and who cover up when they are in the sun. ( Correctly applied sunscreen reduces our ability to absorb vitamin D by more than 90 percent. (8) And not all sunlight is created equal: The sun’s ultraviolet B (UVB) rays—the so-called “tanning” rays, and the rays that trigger the skin to produce vitamin D—are stronger near the equator and weaker at higher latitudes. So in the fall and winter, people who live at higher latitudes (in the northern U.S. and Europe, for example) can’t make much if any vitamin D from the sun. (8) Vitamin D helps ensure that the body absorbs and retains calcium and phosphorus, both critical for building bone. Laboratory studies show that vitamin D can reduce cancer cell growth and plays a critical role in controlling infections. Many of the body’s organs and tissues have receptors for vitamin D, and scientists are still teasing out its other possible functions. New Vitamin D Research: Beyond Building BonesSeveral promising areas of vitamin D research look far beyond vitamin D’s role in building bones. And, as you might expect, the news media release a flurry of reports every time another study links vitamin D to some new ailment. These reports can be confusing, however, because some studies are stronger than others, and any report needs to be interpreted in the light of all other evidence. More answers may come from randomized trials, such as the (VITAL), which will enroll 20,000 healthy men and women to see if taking 2,000 IU of vitamin D or 1,000 mg of fish oil daily lowers the risk of cancer, heart disease, and stroke. Here, we provide an overview of some of the more promising areas of vitamin D research, highlighting the complex role of vitamin D in disease prevention—and the many unanswered questions that remain. Vitamin D and Bone and Muscle StrengthSeveral studies link low vitamin D levels with an increased risk of fractures in older adults, and they suggest that vitamin D supplementation may prevent such fractures—as long as it is taken in a high enough dose. (-) A summary of the evidence comes from a combined analysis of 12 fracture prevention trials that included more than 40,000 elderly people, most of them women. Researchers found that high intakes of vitamin D supplements—of about 800 IU per day—reduced hip and non-spine fractures by 20 percent, while lower intakes (400 IU or less) failed to offer any fracture prevention benefit. () Vitamin D may also help increase muscle strength, which in turn helps to prevent falls, a common problem that leads to substantial disability and death in older people. (-) Once again, vitamin D dose matters: A combined analysis of multiple studies found that taking 700 to 1,000 IU of vitamin D per day lowered the risk of falls by 19 percent, but taking 200 to 600 IU per day did not offer any such protection. () A recent vitamin D trial drew headlines for its unexpected finding that a very high dose of vitamin D increased fracture and fall risk in older women. () The trial’s vitamin D dose—500,000 IU taken in a once-a-year pill—was much higher than previously tested in an annual regimen. After up to 5 years of treatment, women in the vitamin D group had a 15 percent higher fall risk and a 26 percent higher fracture risk than women who received the placebo. It’s possible that giving the vitamin D in one large dose, rather than in several doses spread throughout the year, led to the increased risk. () The study authors note that only one other study—also a high-dose, once-a-year regimen—found vitamin D to increase fracture risk; no other studies have found vitamin D to increase the risk of falls. Furthermore, there’s strong evidence that more moderate doses of vitamin D taken daily or weekly protect against fractures and falls—and are safe. So what is the significance of this study for people who want to take vitamin D supplements? A reasonable conclusion would be to continue taking moderate doses of vitamin D regularly, since these have a strong safety record, but to avoid extremely high single doses. This recent finding does present a challenge to scientists who will work to understand why the extreme single dose appears to have adverse effects. Vitamin D and Heart DiseaseThe heart is basically a large muscle, and like skeletal muscle, it has receptors for vitamin D. () So perhaps it’s no surprise that studies are finding vitamin D deficiency may be linked to heart disease. The Health Professional Follow-Up Study checked the vitamin D blood levels in nearly 50,000 men who were healthy, and then followed them for 10 years. () They found that men who were deficient in vitamin D were twice as likely to have a heart attack as men who had adequate levels of vitamin D. Other studies have found that low vitamin D levels were associated with higher risk of heart failure, sudden cardiac death, stroke, overall cardiovascular disease, and cardiovascular death. (-) How exactly might vitamin D help prevent heart disease? There’s evidence that vitamin D plays a role in controlling blood pressure and preventing artery damage, and this may explain these findings. () Still, more research is needed before we can be confident of these benefits. Vitamin D and CancerNearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed an intriguing relationship between colon cancer deaths and geographic location: People who lived at higher latitudes, such as in the northern U.S., had higher rates of death from colon cancer than people who live closer to the equator. () Many scientific hypotheses about vitamin D and disease stem from studies that have compared solar radiation and disease rates in different countries. These can be a good starting point for other research but don’t provide the most definitive information. The sun’s UVB rays are weaker at higher latitudes, and in turn, people’s vitamin D levels in these high latitude locales tend to be lower. This led to the hypothesis that low vitamin D levels might somehow increase colon cancer risk. ( Since then, dozens of studies suggest an association between low vitamin D levels and increased risks of colon and other cancers. (,) The evidence is strongest for colorectal cancer, with most (but not all) observational studies finding that the lower the vitamin D levels, the higher the risk of these diseases. (-) Vitamin D levels may also predict cancer survival, but evidence for this is still limited. () Yet finding such associations does not necessarily mean that taking vitamin D supplements will lower cancer risk. The trial will look specifically at whether vitamin D supplements lower cancer risk. It will be years, though, before it releases any results. It could also fail to detect a real benefit of vitamin D, for several reasons: If people in the placebo group decide on their own to take vitamin D supplements, that could minimize any differences between the placebo group and the supplement group; the study may not follow participants for a long enough time to show a cancer prevention benefit; or study participants may be starting supplements too late in life to lower their cancer risk. In the meantime, based on the evidence to date, 16 scientists have circulated a “call for action” on vitamin D and cancer prevention: () Given the high rates of vitamin D deficiency in North America, the strong evidence for reduction of osteoporosis and fractures, the potential cancer-fighting benefits of vitamin D, and the low risk of vitamin D supplementation, they recommend widespread vitamin D supplementation of 2000 IU per day. () Vitamin D and Immune Function
Vitamin D and Multiple Sclerosis: Multiple sclerosis (MS) rates are much higher far north (or far south) of the equator than in sunnier climes, and researchers suspect that chronic vitamin D deficiencies may be one reason why. One prospective study to look at this question found that among white men and women, those with the highest vitamin D blood levels had a 62 percent lower risk of developing MS than those with the lowest vitamin D levels. () The study didn’t find this effect among black men and women, most likely because there were fewer black study participants and most of them had low vitamin D levels, making it harder to find any link between vitamin D and MS if one exists. Vitamin D and Type 1 Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes is another disease that varies with geography—a child in Finland is about 400 times more likely to develop it than a child in Venezuela. () Evidence that vitamin D may play a role in preventing type 1 diabetes comes from a 30-year study that followed more than 10,000 Finnish children from birth: Children who regularly received vitamin D supplements during infancy had a nearly 90 percent lower risk of developing type 1 diabetes than those who did not receive supplements. () Other European case-control studies, when analyzed together, also suggest that vitamin D may help protect against type 1 diabetes. () No randomized controlled trials have tested this notion, and it is not clear that they would be possible to conduct. Vitamin D, the Flu, and the Common Cold: The flu virus wreaks the most havoc in the winter, abating in the summer months. This seasonality led a British doctor to hypothesize that a sunlight-related “seasonal stimulus” triggered influenza outbreaks. () More than 20 years after this initial hypothesis, several scientists published a paper suggesting that vitamin D may be the seasonal stimulus. () Among the evidence they cite:
A recent randomized controlled trial in Japanese school children tested whether taking daily vitamin D supplements would prevent seasonal flu. () The trial followed nearly 340 children for four months during the height of the winter flu season. Half of the study participants received pills that contained 1,200 IU of vitamin D; the other half received placebo pills. Researchers found that type A influenza rates in the vitamin D group were about 40 percent lower than in the placebo group; there was no significant difference in type B influenza rates. This was a small but promising study, and more research is needed before we can definitively say that vitamin D protects against the flu. But don’t skip your flu shot, even if vitamin D has some benefit. Vitamin D and Tuberculosis: Before the advent of antibiotics, sunlight and sun lamps were part of the standard treatment for tuberculosis (TB). () More recent research suggests that the “sunshine vitamin” may be linked to TB risk. Several case-control studies, when analyzed together, suggest that people diagnosed with tuberculosis have lower vitamin D levels than healthy people of similar age and other characteristics. () Such studies do not follow individuals over time, so they cannot tell us whether vitamin D deficiency led to the increased TB risk or whether taking vitamin D supplements would prevent TB. There are also genetic differences in the receptor that binds vitamin D, and these differences may influence TB risk. () Again, more research is needed. () Vitamin D and Risk of Premature DeathA promising report in the Archives of Internal Medicine suggests that taking vitamin D supplements may even reduce overall mortality rates: A combined analysis of multiple studies found that taking modest levels of vitamin D supplements was associated with a statistically significant 7 percent reduction in mortality from any cause. () The analysis looked at the findings from 18 randomized controlled trials that enrolled a total of nearly 60,000 study participants; most of the study participants took between 400 and 800 IU of vitamin D per day for an average of five years. Keep in mind that this analysis has several limitations, chief among them the fact that the studies it included were not designed to explore mortality in general, or explore specific causes of death. More research is needed before any broad claims can be made about vitamin D and mortality. () Sunday, February 10 2013
Preparation Time: 10 minutes Cooking Time: 3 minutes Serves: 4 This recipe is to make really healthy protein pancakes. The ingredients provided will make about 4 pancakes but you can make them how big or small you want. Ingredients
Steps
Wednesday, January 23 2013
Remember when a total cholesterol reading of under 200 was the standard for judging cardiovascular health? Today, of course, we know that it's the components of cholesterol (LDL, HDL, the size of those cholesterol particles, and triglycerides) that are much more predictive of heart health. Well, our understanding of total weight and its effects upon your heart has evolved in similar fashion. It's not your total weight but the characteristics of that weight—how much is fat and where it's deposited—that matter most.
Surprised? Thank the scientists at the Mayo Clinic, who are behind this recent discovery. After comparing various health markers with the weights and body mass index numbers of thousands of adults, they found that more than half of those with normal weights and BMIs actually had "high body-fat percentages as well as heart and metabolic disturbances." In other words, they had the same risks of coronary disease, diabetes, and other chronic illness as people who weighed much more. This research, and its sobering implications for millions of Americans, led to the establishment of a new condition called normal weight obesity (NWO). This is more than just the latest fat phobia. It's worth paying attention to because the accumulation of fat in the body, especially in the belly and around internal organs, causes low-level inflammation that gradually damages tissue and blood vessels. (Think of it as metabolic rust.) So even though your weight or BMI may be within acceptable limits for your height and age, don't be lulled into a false sense of security. Do your own analysis, starting with these steps: 1. Stop being preoccupied with pounds. As with total cholesterol, total weight is just one general assessment of your health. Yes, people who are trying to lose weight are more likely to succeed if they weigh themselves often. But seeing numbers that are within a healthy BMI range may actually disguise your heart disease risk. Keep them in perspective. 2. Measure your body fat. For a quick estimate of this key factor, wrap a cloth measuring tape around your naked waist just above your belly button. If your weight is fairly normal but the number you see above your navel is 35 inches or more (40+ inches for men), you may have NWO. For a more exact reading, ask your doctor (or health club) to measure your body fat. This can be done using a variety of noninvasive methods. If it's higher than 30 percent (20 percent for men), you likely have NWO. 3. Get a blood test. Ask your doctor to order a thorough blood analysis at your next physical. Warning signs of NWO include low HDL (total cholesterol and LDL may be normal), along with elevated triglycerides, blood sugar, and blood pressure. 4. Target belly fat. If you're diagnosed with NWO, take aim at visceral fat. Despite how entrenched it may seem, you can lose it. The keys are: Avoid the white stuff (white bread, rice, pasta, and other refined carbohydrates). Add monounsaturated fats, which target belly fat, to your diet. And do interval exercises to burn more fat and strength-training to build lean body mass. 5. Keep tracking fat. Just as you hop on the scale to keep tabs on your weight, do the same with your body fat. Have it measured periodically at your doctor's office or health club. Or just observe the notches where your belt buckles. Conversely, if you're considered overweight by current standards, there may be some good news here. If your body-fat percentage is lower than 30 percent (20 percent for men) and your blood chemistry is normal, then you are among the "fat and fit." (Many athletes are in this category.) Continue to eat smart and exercise, but accept your body for what it is and know you're not unhealthy because of it. Feeling fat and feeling healthy are no longer mutually exclusive. More Heart-Healthy AdviceStaying hydrated is one simple way to keep blood pressure in the safe zone.Monday, January 07 2013
 © Betty Shepherd
Sports massage is a form of massage therapy that is tailored to treat the needs of athletes. The use and application of specific techniques is the foundation of sports massage, yet what distinguishes it from other modalities is the intention behind the therapy. Many of us might think of massage as relaxing and holistic. Sports massage, in contrast, is designed to achieve specific goals, such as increasing performance or treating or preventing injury. The purpose of a sports massage session can vary, depending upon numerous factors that are unique to each athlete. For instance, sports massage can be used effectively to treat conditions such as tendonitis, strains, sprains, and adhesions. It can also be used in conjunction with training schedules and conditioning programs to enhance performance, aid in recovery and reduce the potential for injuries. The major applications of sports massage are recovery, remedial (to improve a debilitating condition), maintenance, and event (pre, inter, and post). An athlete can enhance his or her performance by knowing when to incorporate sports massage into a training routine. Healthy, injury-free muscles perform better, longer, and with less chance of injury. Sports massage can help to optimize the positive factors that affect performance, such as healthy muscle and connective tissues, normal range of motion, high energy and fluid and pain-free movement, as well as inducing mental calm and improving alertness, and concentration. It also can help minimize negative factors such as dysfunctional muscle and connective tissue, restricted range of motion, low energy, staleness, pain, and high anxiety(1a). Sports massage decreases injury potential by helping to prevent acute injuries (muscle tears) as well as chronic injuries stemming from wear and tear (tendonitis). Regular massage allows the muscles and soft tissue to stay supple and healthy, lengthened and flexible and free from adhesions, thereby reducing the potential for injury. By increasing circulation and assisting the body’s healing processes and breaking down scar tissue and adhesions, sports massage can help chronic injuries get better. Important Primary and Secondary Effects of Sports Massage(1b)Primary effects refer to the physiological and psychological condition of the athlete and include:
Secondary effects refer to performance-related outcomes and include:
If you decide that sports massage is the right treatment for you, it is important to find a well-trained therapist. Check out if a practitioner has had training in sports massage from an accredited school. Currently, there is no national credentialing that signifies a person who has passed a test demonstrating a solid understanding of the foundations and techniques of sports massage, so you will have to ask a few questions. How many hours of training (in general) did they have? Was their school accredited by the American Massage Therapy Association? How many hours of training in sports massage did they receive? What kind of athletes have they worked with? Were the athletes training or competing at the time? Is your therapist an athlete (on any level)? Many sports massage practitioners participate in races or competitive events, which increases their understanding not only of the uses and benefits of sports massage, but of other factors that go into being an athlete. For example, the length of time between the massage session and the athletic event directly relates to the depth of pressure a therapist should use. A knowledgeable therapist will know that a pre-event massage, which is meant to encourage general looseness, calls for less deep work than a regular “maintenance” massage. It is important that your therapist always errs on the side of caution when using deep pressure, and that they have an understanding of the psychology of an athlete and the physical demands of training. One of the benefits of working regularly with the same sports massage therapist is that he or she can learn to feel what is “normal” for your tissue and body type and can keep a watchful eye on any changes that may signal the need to head off potential trouble spots. If an injury does occur, the therapist can join the team of health care practitioners helping you to recover. Here, the focus is on healing the injury quickly and effectively, minimizing the side effects of the injury and decreasing the chance of re-occurrence. The use of sports massage in training routines varies depending on the athlete, the sport being trained for and the level of competition. It is important to mention that every athlete and every situation is going to be different, and that each person should research and find a plan that is most suitable for them. With that in mind, let’s take a look at how two different athletes used sports massage in conjunction with their training. When Uta was competing in 5K to 10K races, or preparing for a marathon, she received sports massage twice a week. Usually, she scheduled her massages the day after one of her harder training sessions for the week. If that wasn’t possible, she would allow herself a treatment session on the same day as her hard workout, but she would wait at least 3 to 4 hours to let her body recover some from the training before addressing soft tissue needs. Getting regular massage during her intense training periods also helped Uta psychologically, by allowing her to give back to her body and take some time for herself. Training for my first triathlon, I used sports massage regularly. I noticed that I could identify potential problems and head them off before they became an impediment in my training. I also felt, during the most intense training periods, that taking the time to give back to my body really helped me to feel like I was rounding out my training program. Having time to recover, making the effort to work my muscles and being in tune with my body, all played integral roles in my ability to train as hard as I did, without hurting myself. Getting regular massages during training is a great way to generate feedback for yourself about how you are doing. The more feedback you can gather about performance and training, and how your body is responding to it all, the better informed you will be about how you can compete and recover from competition. Sports massage, therefore, can be a great tool for athletes in their training. It provides myriad benefits, including increasing performance potential, speeding recovery time, and reducing the prevalence of injuries. And let’s not forget the wonderful relaxation, stress relief, and whole body integration that everyone—not just the athlete—can obtain from massage! Wednesday, December 12 2012
This Indonesian dish packs a massive flavour punch and is quick and easy to make. Ingredients
Steps
Other Dietary Information
Saturday, July 28 2012
 © Betty Shepherd
When you decide on your favorite summer workouts—we discussed a few fun options in Part I—you can move on to organize everything so you stay healthy and well-hydrated during your fitness routine. First of all, add extra care to how you prepare for your workouts. Make sure you are properly hydrated beforehand. Drink small amounts of water frequently, beginning two hours before you go out. I would not necessarily drink too much for 20 to 30 minutes prior to your start, though, because it can make you need to “go” while working out. If you plan to work out for more than one hour, you might want to run with a water bottle belt, as many athletes do. You also could leave one or more water bottles on the course. If you decide on that strategy, it is best to stay on a loop course. This gives you a chance to replenish every few miles. And, if you want to be absolutely safe, ask a friend to join you on a bike. For bikers, use both your water bottles, and stay ahead of the game by stopping at any convenience store or gasoline station to fill-up your bottles before you need them again. Listen to Your Body, Stay HealthyNothing is more important than listening to your body. If you do not feel well, please be very cautious. Before, during, and after your workouts, the first signs of a possible problem might be heavier breathing, an elevated heart rate, or losing concentration. Consider wearing a heart rate monitor—it can caution you before you run into trouble. When you feel unwell, admit it to yourself early on and get out of the heat right away. Cool off with a cold towel, use ice cubes, and hydrate! Please, do not wait to see a physician if you do not feel better immediately. Be familiar with some of the early warning signs of overheating: dizziness, fainting, fatigue, hot skin and followed by chills, lack of perspiration, feeling thirsty, and elevated heart rate. If you stop sweating, you most likely are very dehydrated(1). Also be careful after your workout. Take a dry shirt to put on after your run, and always take some fluid to drink. If you feel cold—even in summer, for example when you come from outside into an air-conditioned room while still wearing your wet workout clothes—change immediately into dry clothes. It may be summer, but you need to stay “warm” after your workouts to avoid weakening your immune system and maybe getting a cold. For adequate protection, sunscreen, glasses, a summer hat, and a rain jacket are always good to have close by. Hydrate Well Throughout the Day © Betty Shepherd It can be very warm and dry during the summer, so make sure you stay cool and hydrated at all times. There are some guidelines I would suggest, and one of my favorite is to keep a bottle of water or a sports drink close by. This will remind you to drink and get replenished with small amounts continuously and evenly spread out throughout the day. Hydration is critical for many body functions, such as digestion, regulation of body temperature, and the circulatory processes that bring nutrients to the cells and transport waste from them. This is even more understandable when considering that our bodies are up to 75% water in total, depending on age and build, with blood being 83% water and the brain being 75 to 78% water. These are the levels when each of those organs work best(2). When you get dehydrated, every cell in your body suffers, causing you to feel less fit and fatigued(3). This puts more stress on your body and makes you more prone to illness and disease. And you can be at risk of overheating, which can have terribly serious consequences—including being life-threatening. For proper hydration, start with juice from a fresh squeezed lemon with lots of water first thing in the morning. It is good for re-hydration after your night’s sleep and also will help your body to detoxify. And as mentioned earlier, drink enough before, if possible during, and right after your training. It is best to replenish within 30 minutes of finishing your workout—the so-called “recovery window.” I like to eat a big slice of water melon right after my training, it is a great source of water, antioxidants, and easily digested carbohydrates. In the following article “General Guidelines,” you can find more information on this topic. A Few Thoughts on Summer Nutrition © Betty Shepherd Many people like to adjust their nutrition and take advantage of everything that is fresh and more available in the summer, like tasty fruits and vegetables. It is berry season—maybe you are lucky enough to be able to pick your own on a berry farm. Eat food that has high water content like melon, citrus fruits, berries, and vegetables. Diluted fruit juices with 1 part juice and up to 2 parts water can help you to stay hydrated. The juice from sour cherries, for example, has many health benefits and can even support faster strength recovery for runners. You also can try the many different kinds of unsweetened iced teas. My favorite flavor is mango. Enjoy what you eat and make it tasty. Add some cool summer nutrition like different kinds of smoothies. Depending on the amount you make, they even can be served as an entire meal. Just add water, berries (like raspberries and blueberries), banana, whey protein, and some ice cubes into a blender. Mix it and enjoy. Or try a variation with mango or pineapple. And for more health benefits, add a teaspoon of ground flaxseeds. There also are many delicious salad creations with great dressings. You could try a variety of citrus dressings. Other choices of salads include my favorites—fresh cucumber salad with dill and onions or a tomato salad with olives, feta, and basil. Sashimi and sushi can be delightful lighter dinner fare when well-portioned. And when you prepare your meals, add more vegetables than pasta or potatoes. And how about cold summer soups like water cress and gazpacho? And for all you BBQ lovers, here are some thoughts on “Healthier Grilling.” I hope you can enjoy many relaxing summer evenings with your family and friends. Good luck for your summertime fitness!
Sunday, June 10 2012
 © Betty Shepherd Summer is such a beautiful time of the year. Happy days with stunning sunrises, long, warm evenings and relaxing afternoons freshened up with lemonade and watermelon. Even on hot days, it is not difficult to find great exercises to keep your fitness level up. Summer is also special because you can finally do the workouts you might have been missing during the colder months of the year. You even can take advantage of the training sessions you would not necessarily do during the ideal training period for other sports in winter. You can add cross-training, as well. That means you can work out in other sports or add exercises that support what you normally focus on. It gives you an opportunity to prepare yourself for your upcoming autumn events or improve your fitness and skills for your favorite winter sports. Cross-training can give you a wide variety of workout choices which can enable you to reach your goals. In the summer, you have a wonderful opportunity to take advantage of the outdoors and experience beautiful connections to nature—the oceans, lakes, rivers, beaches, mountains, and shady woods and forests. Before we go on, however, I would advise getting a physical before you start your summertime fitness, making sure you are fit enough to work out in those warm conditions and are able to stay ahead of the game. It is a time that is good for more than just goal setting. You also can talk about your fitness ideas and workout possibilities for the upcoming months and decide if they are realistic for you. Your Favorite Summer WorkoutsOf course, in summer—as well as year-round—do activities you enjoy. They might include your favorite ball game, long hikes, water sports, or anything that is giving you excitement and happiness while exercising. Maybe you have some “wishes” you can turn into goals—like improving your fitness, learning to surf, running your first 5K, hiking a mountain, or biking some new trails by the end of the warmest time of the year. When you follow a path of realistic and achievable short-term goals, it can be much easier to stay motivated and make it fun to reach your goal.  © Betty Shepherd It always is a good idea to include your favorite workouts first, then, integrate new opportunities as the summer progresses. By the end of the warmest months, you will have explored and tried different exercises—alternatives you may have been curious about, perhaps, and had thought could be fun for you. Ball games, swimming, water sports, mountain biking, running, hiking, camping, for example, all are great exercises to try during the summer, especially if you had never done so before or if it had been a long time since you did them. And if you are ready to take on multiple challenges, nothing might be better than combining a number of activities. My favorite summer workouts are those easy and relaxing evening runs, when the sun starts to set and the air is getting fresher, when I can play with those long shadows in the forest. I often combine them with a swim, diving into a lake after my run. Sometimes I jog a few miles to a beach by a lake and cool-off by swimming for some distance, depending on how I feel after my run. I used to do this often as a kid and later during my track season. I have enjoyed it ever since. As the previous comment illustrates, summer workouts are a great way of rekindling happy childhood memories: those long days of carefree summer vacations from school, playing baseball, basketball, or soccer, or maybe completing a track session in the stadium. Perhaps you have a loving memory of the smell of freshly cut grass. That wonderfully distinctive aroma always reminds me of the newly-mown infield at the local track when I was a kid. During the warmest time of the year, it is best to wait for temperatures to have fallen in the early morning or the late evening. Any kind of ball game—basketball, baseball, soccer, or tennis—is fun to play in the cooler evenings. With dusk still far away, you can arrange to get together with your friends after work and add informal versions of these games to your other activities. This can be fun and often makes it easier to stay fit. When I was growing up and started running, we played lots of ball games as warm-ups for our training sessions. A game of team handball or volleyball was just right for us kids. Coming from Germany, soccer always was the favorite. Maybe you can join a group of friends to play a game? You will soon find the countless sprints to get the ball or trying to keep it will definitely give you good cardiovascular exercise. Huffing and puffing, I sometimes had to stop running to catch my breath. For many of us, nothing is nicer than taking part in summer water sports. You can enjoy the whole day at a lake or the ocean with activities such as paddle boarding, kayaking, surfing, snorkeling, or playing different water ball games with your friends. These all are sports that can provide fun activities for you and your entire family. If you don’t have the luxury of a few free days, try a nice swim before or after work, or, if time permits, during your lunch break. Swimming is not only a great cardiovascular workout, and refreshing during the summer months, it also can help you recover from more strenuous training like biking or running. And, at the same time, it will improve deeper breathing.  Dave enjoys kayaking across the state of Florida. © Dave Bracknell A former client of mine started with a few sprint triathlons in the summer and quickly moved up to the Olympic distance in winter. He later discovered that kayaking would be fun for him, too. I got an email message from him with breathtaking photos of the ocean and his kayak resting on a beach. He wrote that he just kayaked across the state of Florida in a charity event. I can imagine that he had a fun pool party afterwards! It is a great idea to start a party with your family and friends in late afternoon, playing ball and enjoying swim games, and later taking in the sunset while having a super-tasty barbecue. Could an interesting hike become one of your favorite workouts? Even a leisurely “glow worm and fire flies” hike on a cool summer night might be something you would enjoy. It can be such a fun activity for the whole family. And if you choose a long day hike, you might want to top it off by camping out overnight under the stars. Change the Venue, Adjust Your Goals, and Explore Cross-TrainingSure, you want to avoid the hottest part of the day—so go inside! Join a gym for the warmest months, and instead of running or biking outside, try the treadmill or the stationary bike or one of the many other aerobic exercise machines available at most gyms. You always can exercise outside during the cooler temperatures around sunrise and sunset. The nice thing about summer events is that most of them take place in the morning or evening hours. Nothing is better than completing your workout or event and meeting friends for a late breakfast afterwards. “It’s just a piece of pancake!” Adjust your fitness goals for the warmest time of the year. As always, it is best to set realistic, achievable, short-term goals. I recommend focusing on a few shorter workouts with higher intensity and playful variations in speed. Perhaps your goal might be to become faster in your sport during the summer. Then in autumn, you can add some endurance and focus on longer events again. Once you accomplish your summer goals, you can use your improved fitness to achieve great results in your events later in the year.  © Betty Shepherd Here are some ideas. If you are a triathlete, you might want to improve one of your disciplines to be better prepared for competition in the fall. To work on your swimming might be a good idea. Or you might change from running to more biking, and in the colder months add longer running workouts again. There are great duathlon competitions in the summer. To work on improving your speed, you may decide to prepare for a sprint triathlon or a sprint duathlon, instead of the longer versions. Many runners may just have finished a spring marathon. The warm summer months are ideal to prepare for a 5K, and in late August one could prepare for a 10K. Then, in September, you can get ready for a half marathon. All the training and goal setting can be done with the ultimate aim of a faster marathon. Or simply enjoy the shorter distances as your main event all summer. That is good, too! You also can switch from one sport to another. Think “off season training.” For runners, bike and swim instead of doing high mileage running. Some bikers go from the road into the forest and mountain bike, it is a great way to improve your skills. Enjoy water sports like kayaking or paddle boarding. Compete in team swimming events, relays are always great fun. A good goal could be to work on other elements of fitness, like strength or technique training, especially if these are areas in which you already want to improve. To do this, you may want to include these new elements in your routine during the summer so you are better prepared for your upcoming events later in the year. I love these elements of cross-training. They can give you a chance to try out a variety of workouts—not doing the same activity every day. And they can be done indoors during the warmest hours of the day. Think about it as something you can look forward to complement your training. Deep-water running, core strengthening, light weights, stretching and yoga… they all can be added to your summertime fitness routine. In this manner, you can condition your body for your fall events—to be a better runner, biker, or golfer—and for your winter sports to be a stronger skier, snowboarder, or skater. Be prepared to adjust your workouts according to the weather conditions on any given day. It can be hot, humid or rainy, and setting a new and easier goal will help you achieve them. Maybe you, too, would love to combine some of your runs with a cooling swim afterwards. And finally, a general suggestion for your summer workouts: start them slowly, increasing your workload in gentle increments. The weather conditions can be challenging and even deceptive. By starting your workouts carefully, keeping your strength in reserve, you will be able to keep your body temperature and your pulse lower. And you will not get so fatigued. In many climates, temperatures can change dramatically over the course of the day, so always be aware of the conditions in which you do your activities and training. Of course, during summer months, adequate hydration should always be on your mind. Fitness Programs and Sport Events You Can JoinCheck out recreational leagues and programs for adults and kids in your area. Your town, local fitness club, and local businesses might offer programs for many sports and events, and maybe you would like to join one of them. This way you also might meet new friends and enjoy staying fit together. It might even not feel like working out hard at all. There are many events over the summer that may be of interest to you. Some of them are charity rides or runs where you also can get the satisfaction of helping your community or a charity that touches your heart like SOS Outreach with which Take The Magic Step is a partner. In “Summertime Fitness: Part II,” I will explore proper hydration and offer a few thoughts on summer nutrition. Until then, I hope you can enjoy your fun and cool summertime fitness!
|
 |
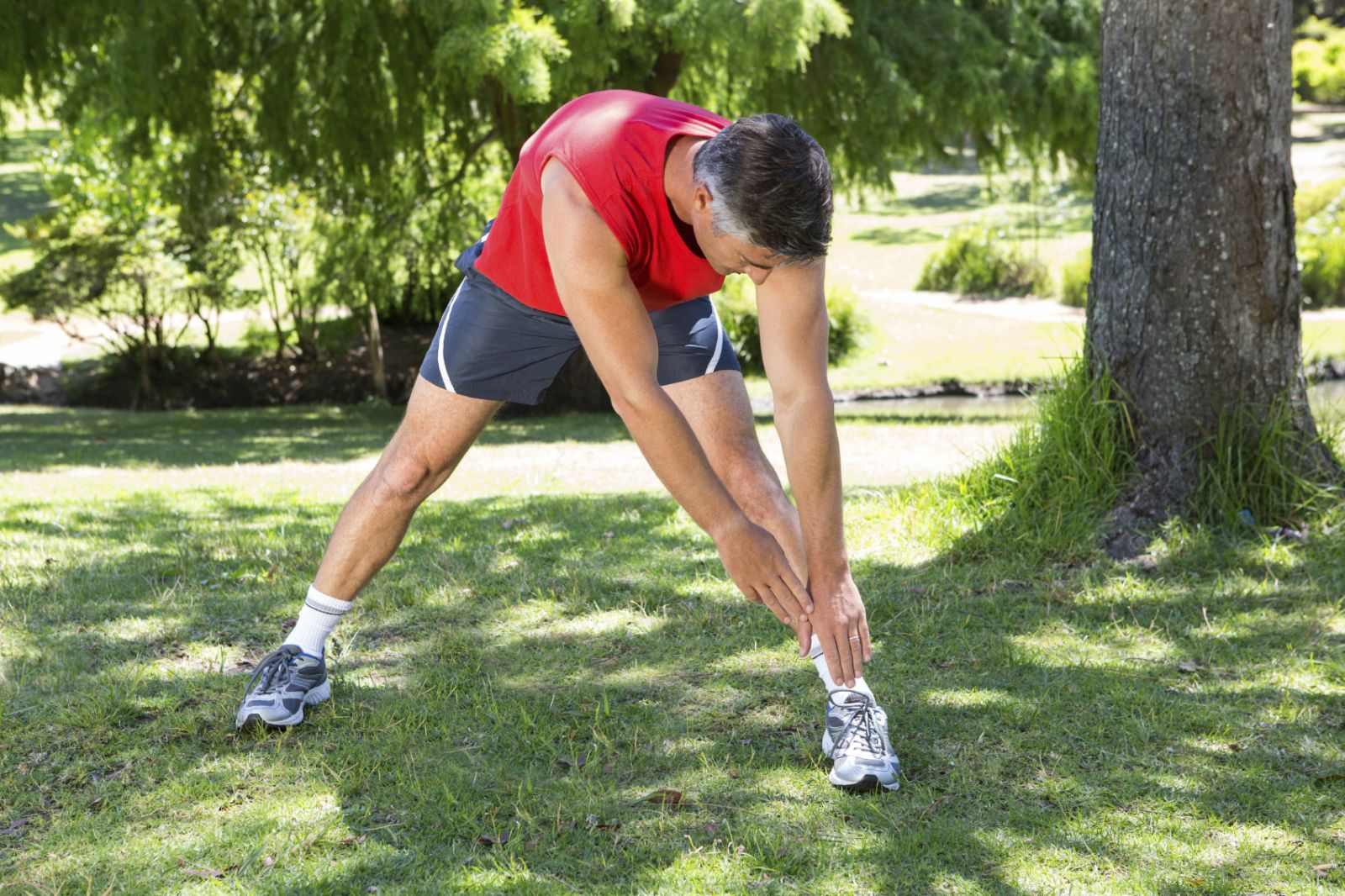


 Image: iStock
Image: iStock breaks. Bone strength in later life depends upon your peak bone mass in youth. An active lifestyle in youth can increase maximum bone density.
breaks. Bone strength in later life depends upon your peak bone mass in youth. An active lifestyle in youth can increase maximum bone density.

 Vitamin D’s role in regulating the immune system has led scientists to explore two parallel research paths: Does vitamin D deficiency contribute to the development of multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes, and other so-called “autoimmune” diseases, where the body’s immune system attacks its own organs and tissues? And could vitamin D supplements help boost our body’s defenses to fight infectious disease, such as tuberculosis and seasonal flu? This is a hot research area and more findings will be emerging.
Vitamin D’s role in regulating the immune system has led scientists to explore two parallel research paths: Does vitamin D deficiency contribute to the development of multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes, and other so-called “autoimmune” diseases, where the body’s immune system attacks its own organs and tissues? And could vitamin D supplements help boost our body’s defenses to fight infectious disease, such as tuberculosis and seasonal flu? This is a hot research area and more findings will be emerging.